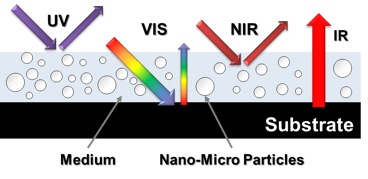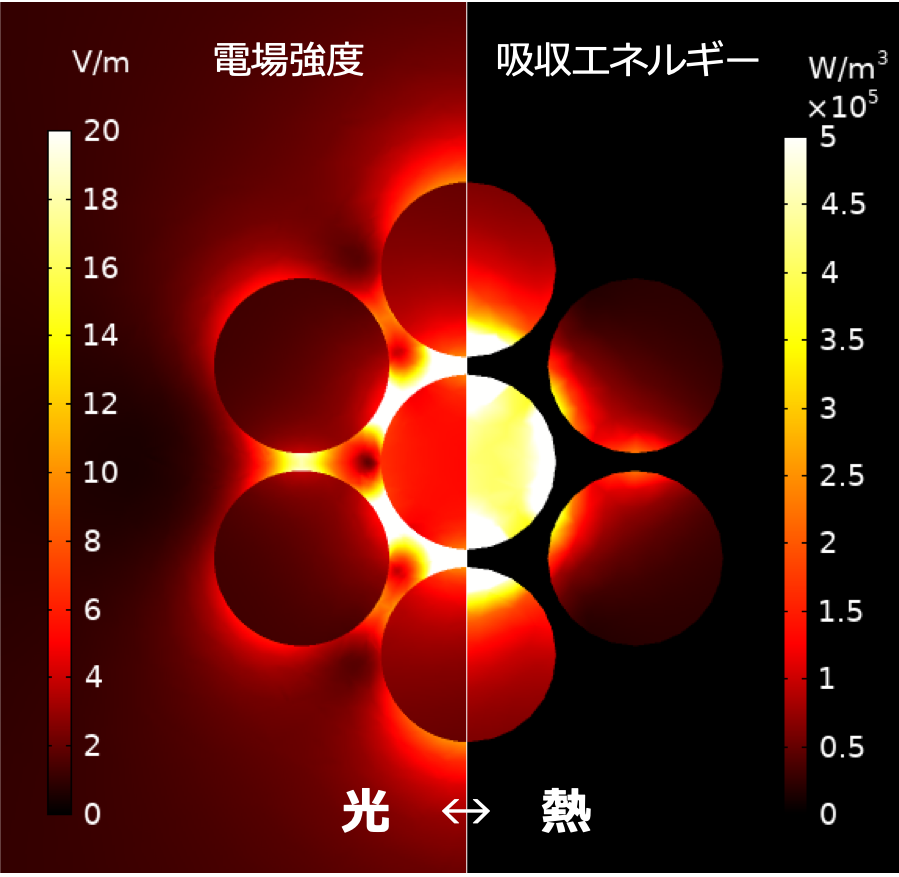
In order to secure sustainable modern energy (SDGs, Goal 7), it is important to develop technologies for effective utilization of solar energy by using photothermal conversion. In this research, we aim to clarify the photothermal conversion principle, to surpasses the heat energy recovery performance from light. We aim to create a new trend of design technology in energy transport mechanisms using electromagnetic waves.
持続可能な近代的エネルギーの確保(SDGs目標7)のため、光と熱の変換を利用した太陽光エネルギーの有効利用技術の発展は重要な課題です。本研究では、光と熱はどのような物理でエネルギー交換しているか(光熱変換原理)を明らかにし、これまで実現されてきた光からの熱エネルギー回収性能を超える新たな熱輸送制御技術の確立を目指すと共に、電磁波を利用したエネルギー輸送機構における新たな設計技術の潮流の創発を目指します。

本研究は科学技術振興機構(JST) 創発的研究支援事業の助成を受けております。
Reference Keywords: Photothermal cancer therapy, Plasmonics fluids, Solar energy